Lexical Summary Kemosh or Kemish: Chemosh Original Word: כְּמוֹשׁ Strong's Exhaustive Concordance Chemosh Or (Jer. 48:7) Kmiysh {kem-eesh'}; from an unused root meaning to subdue; the powerful; Kemosh, the god of the Moabites -- Chemosh. NAS Exhaustive Concordance Word Originof uncertain derivation Definition a god of the Moabites NASB Translation Chemosh (8). Brown-Driver-Briggs כְּמוֺשׁ proper name, of a divinity Chemosh (כמש MI3. 5. 9. 12. 13. 14. 18. 19. 32. 23 also עשתר כמש Jeremiah 1:17 and proper name, masculine כמשמלך Jeremiah 1:1; Assyrian Kammusunadbi, a king of Moab SchrCOT i, 281; = KAT2, 288; compare further BaeRel 13 f. 238, 256 NöZMG 1888, 471; ᵐ5 Ξαμώς); — god of the Moabites to whom Solomon erected a high place 1 Kings 11:7,33; 2 Kings 23:13; Jeremiah 48:7 (Kt כמישׁ), Jeremiah 48:13. Moab is ׳עַםכֿ Numbers 21:29 (ode) people of Chemosh, and Moabites his sons and daughters, compare Jeremiah 48:46. He is said to be also the God of the Ammonites Judges 11:25 (probably an error BaeRel 15 GFM). כמז (√ of following; meaning dubious; Arabic כמישׁ Jeremiah 48:7 Kt, see כְּמוֺשׁ. above כמן (√ of following (si vera l); perhaps be hidden; compare Aramaic כְּמַן, Topical Lexicon Name and Identity Chemosh is presented in Scripture as the national god of the Moabites. His worship was the distinguishing mark of Moabite religion, paralleling Baal among the Canaanites and Milcom among the Ammonites. The biblical record consistently associates Chemosh with detestable practices, placing him in direct opposition to the covenant God of Israel. Occurrences and Narrative Settings Numbers 21:29 introduces Chemosh in a poetic taunt: “Woe to you, O Moab! You are destroyed, O people of Chemosh!” Here the conquest of Moab by the Amorite king Sihon is portrayed as evidence of Chemosh’s impotence, foreshadowing Moab’s future downfall. Judges 11:24 records Jephthah’s argument to the Ammonites: “Will you not possess what your god Chemosh has given you?” Though Chemosh was actually the god of Moab, Jephthah lumps together the eastern peoples’ gods to highlight that Israel will likewise keep what the LORD has given her. The passage underscores the exclusivity of Israel’s claim to her inheritance. 1 Kings 11:7 reveals Solomon’s tragic apostasy: “At that time on a hill east of Jerusalem, Solomon built a high place for Chemosh, the abomination of Moab.” By accommodating foreign worship, the king facilitated syncretism that ultimately divided the kingdom (1 Kings 11:33). 2 Kings 23:13 records Josiah’s reform: he “defiled the high places east of Jerusalem… which Solomon king of Israel had built… for Chemosh the abomination of Moab.” The prophetically driven purge demonstrates God’s enduring demand for covenant purity. Jeremiah devotes a significant oracle to Moab. The prophet declares, “For because you trust in your works and treasures, you also will be captured. Chemosh will go into exile” (Jeremiah 48:7). In verse 13 he adds, “Moab will be ashamed of Chemosh, just as the house of Israel was ashamed of Bethel.” The climactic pronouncement in verse 46 laments, “Woe to you, O Moab! The people of Chemosh are destroyed.” Repeated references intensify the assertion that Chemosh cannot deliver, and that ultimate sovereignty belongs to the LORD. Historical Background Outside the Bible, the Mesha Stele (ninth century BC) confirms Chemosh’s centrality in Moabite life. King Mesha credits Chemosh for victory over Israel and reports that captured Israelites were offered to the deity. Such extrabiblical data align with the biblical depiction of Chemosh worship as violent and degrading, often involving child sacrifice (implicitly condemned in 2 Kings 3:26–27). Israel’s proximity to Moab along the eastern side of the Dead Sea meant continual cultural pressure. Solomon’s political marriages opened the door for official recognition of Chemosh in Jerusalem. Two centuries later, Josiah’s reforms show how deeply entrenched that influence had become. Theological Significance 1. False hope: Chemosh epitomizes the futility of trusting in idols. Jeremiah’s oracles project Chemosh into exile alongside his worshipers, dramatizing the impotence of man-made gods. Lessons for Today • Reliance on any power, ideology, or possession other than the living God mirrors Moab’s trust in Chemosh and is destined to fail. Forms and Transliterations וְלִכְמוֹשׁ֙ ולכמוש כְּמ֑וֹשׁ כְּמ֥וֹשׁ כְמֹושׁ֙ כמוש לִכְמוֹשׁ֙ לכמוש מִכְּמ֑וֹשׁ מכמוש chemoVosh kə·mō·wōš ḵə·mō·wōš keMoosh kəmōwōš ḵəmōwōš lichmoVosh liḵ·mō·wōš liḵmōwōš mik·kə·mō·wōš mikkeMoosh mikkəmōwōš velichmoVosh wə·liḵ·mō·wōš wəliḵmōwōšLinks Interlinear Greek • Interlinear Hebrew • Strong's Numbers • Englishman's Greek Concordance • Englishman's Hebrew Concordance • Parallel TextsEnglishman's Concordance Numbers 21:29 HEB: אָבַ֖דְתָּ עַם־ כְּמ֑וֹשׁ נָתַ֨ן בָּנָ֤יו NAS: O people of Chemosh! He has given KJV: O people of Chemosh: he hath given INT: are ruined people of Chemosh has given his sons Judges 11:24 1 Kings 11:7 1 Kings 11:33 2 Kings 23:13 Jeremiah 48:7 Jeremiah 48:13 Jeremiah 48:46 8 Occurrences |
|
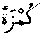 is bunch, heap).
is bunch, heap). 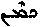 , lie in ambush; Arabic
, lie in ambush; Arabic 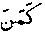 id. is denominative from loan-word
id. is denominative from loan-word 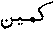 according to Frä243).
according to Frä243). 


